The cultivation of human resources relevant to science and technology is one of the most important basic infrastructures for promoting science and technology. This chapter describes the cultivation of human resources for science and technology in school education, mainly looking at conditions in universities and colleges as higher education institutions. Here, an international comparison of the enrollment status at each phase of higher education, career options after graduation or leaving school, the present situation of adult education, and of degree awarded is attempted.
3.1 The status of the number of students in Japan's education institutions
Chart 3-1 shows the total numbers of students and pupils in school education for FY 2013 in order to gain an overall impression of the education system in Japan. The height of each bar in the graph represents the length of time in terms of course terms in each educational institution and the area of each bar of the graph indicates the number of the students and the pupils enrolled there.
The number of children in elementary schools is about 6,677,000, that of pupils in junior high schools is about 3,536,000, and that of high school students is about 3,311,000 (including only the regular courses).
The number of undergraduate students is about 2,562,000 (including approximately 840,000 in the field of “natural science and engineering” ), and that of college students is about 134,000 (including approximately 18,000 in the field of “natural science and engineering” ). The number of master's program students in graduate schools is about 163,000 (including approximately 102,000 in the field of “natural science and engineering” ) and that of doctoral program students is about 74,000 (including approx 49,000 in the field of “natural science and engineering” ).
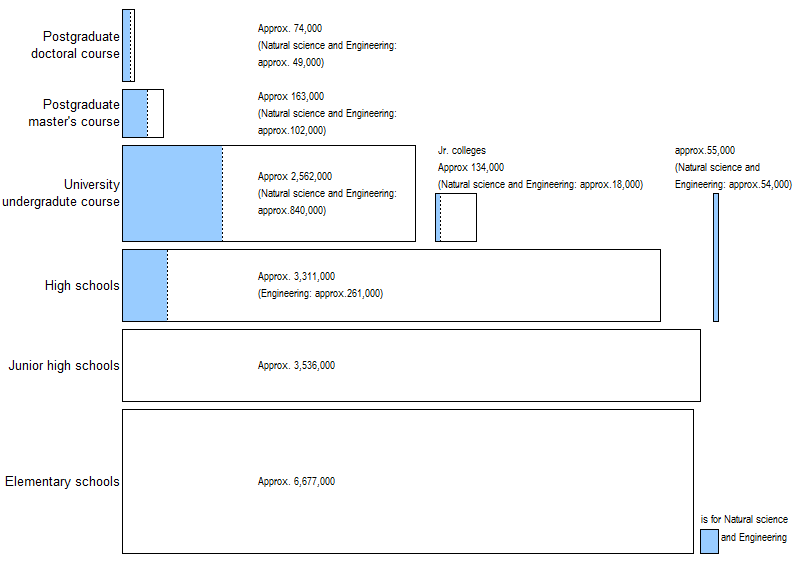
Note:
1) Conceptual representation indicating the breakdown of the number of students and pupils enrolling in the regular courses of each education institution and, of these, the number of students and pupils enrolled in Natural sciences and Engineering (regions shown in blue).
2) “Natural sciences and engineering” for universities and colleges or graduate schools is the total of Natural sciences, Engineering, Agricultural sciences, Medical science, and Dentistry and Pharmaceutical science.
3) “Natural sciences and Engineering” in junior colleges means the “Industrial department” .
4) The height of each bar in the graph represents the length of time in terms of course terms for each educational institution and the area of each bar of the graph indicates the number of the students and the pupils enrolled.
5) The number of students in the postgraduate master's course and postgraduate doctoral course excludes the students in professional graduate school program.
Source:
MEXT, “Report on School Basic Survey”



